Introduction
The pharmaceutical industry is evolving rapidly, with advanced analytics becoming a crucial driving force behind its transformation. This approach emphasizes improving efficiency, cost-cutting, and maintaining high-quality standards. In this blog, we will explore how advanced analytics enhances pharma manufacturing, its applications, and the benefits it brings.
1. Predictive Maintenance
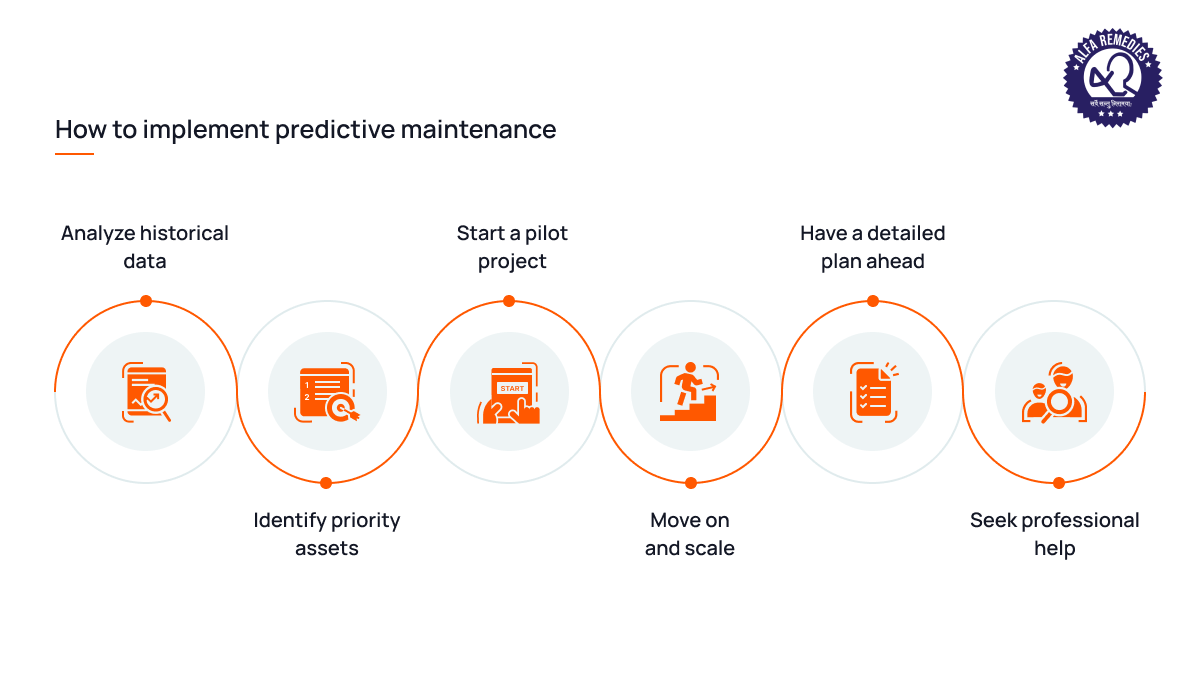
Predictive maintenance involves forecasting equipment failures before they occur. By leveraging advanced analytics, it can analyze sensor data, historical maintenance records, and company experience to anticipate when equipment might break down. This proactive maintenance approach reduces downtime and extends equipment lifespan.
Example: A pharmaceutical company implemented predictive maintenance on its production lines and reduced unplanned downtime by 20%, while also increasing the useful life of equipment by 15%.
2. Process Optimization
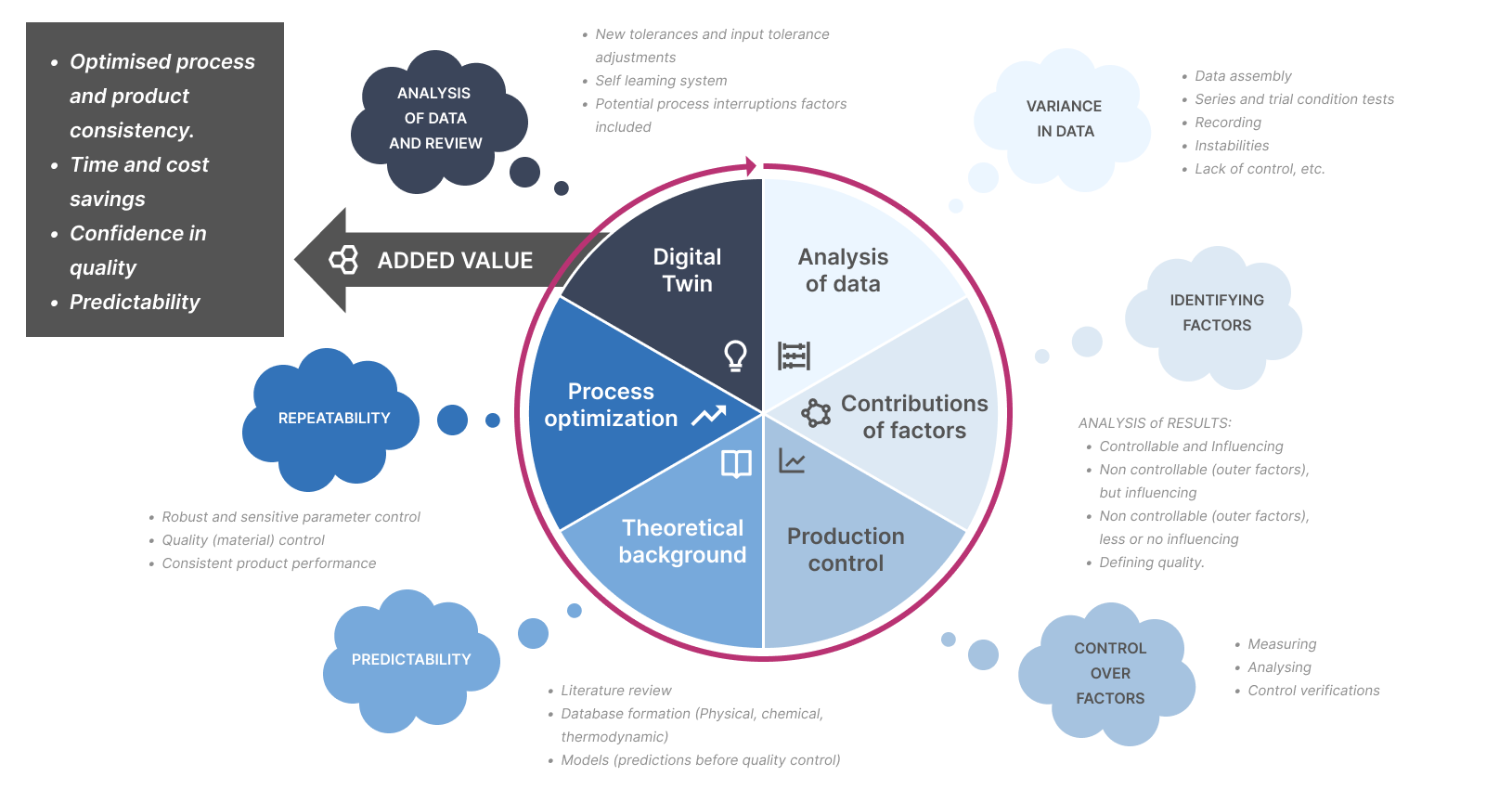
Advanced analytics optimizes the manufacturing process by identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of data, identifying patterns that even the most skilled analysts might overlook, resulting in a streamlined production process.
Example: A pharma manufacturer used advanced analytics to improve its tablet coating process, reducing variability and thus enhancing product quality.
3. Quality Control

Quality control is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Advanced analytics plays a pivotal role in ensuring drug quality by providing real-time monitoring, detecting deviations from standards, and enabling swift corrective actions. This results in fewer substandard products entering the market.
Illustration: A company used real-time analytics in injectable drug production, reducing rejected batches by up to 30%.
4. Supply Chain Management
Advanced analytics streamlines supply chain management by forecasting demand, maintaining optimal inventory levels, and improving supplier performance. This leads to more efficient production schedules, reduced costs, and improved supplier reliability.
Example: A pharmaceutical firm used advanced analytics to optimize its supply chain, reducing inventory costs by 25% and improving on-time delivery rates.
5. Drug Development
In drug development, advanced analytics can significantly speed up the process by analyzing clinical trial data, predicting results, and identifying potential problems early. This can shorten the time it takes for new drugs to reach the market, benefiting patients and pharmaceutical companies alike.
Example: A biotech company leveraged advanced analytics to reduce clinical trial durations by up to 20%, accelerating the delivery of new therapies to patients.
Conclusion
Advanced analytics is revolutionizing pharmaceutical manufacturing, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality. Its applications, from predictive maintenance to supply chain optimization, are reshaping the future of the industry. To stay competitive and meet the growing demands of healthcare, pharmaceutical companies must integrate advanced analytics into their processes.