Skip to content
Enhancing Efficacy, Safety, and Patient Adherence

1. Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine
- Advancements: Nanoparticles, liposomes, and micelles enable targeted drug delivery, improving bioavailability and reducing side effects.
- Impact: Enhanced drug efficacy, reduced toxicity, and personalized treatment options.
2. Controlled Release Systems
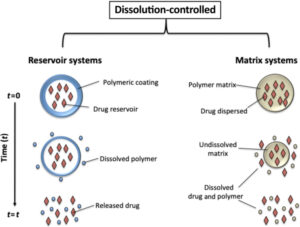
- Innovations: Implantable devices, transdermal patches, and microspheres provide sustained drug release.
- Benefits: Better patient compliance, minimized dosing frequency, and optimized therapeutic outcomes.
3. Personalized Medicine
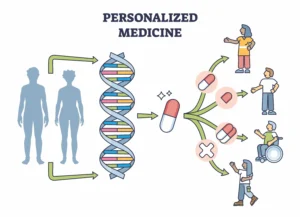
- Approach: Tailoring drug formulations based on individual patient characteristics (genetics, metabolism, etc.).
- Advantages: Precise dosing, reduced adverse effects, and improved treatment response.
4. Biologics and Monoclonal Antibodies

- Breakthroughs: Biologic drugs (e.g., monoclonal antibodies) require specialized manufacturing processes.
- Challenges: Ensuring stability, scalability, and consistent quality.
5. 3D Printing in Pharma Manufacturing
- Revolution: Customized drug formulations, patient-specific dosage forms, and rapid prototyping.
- Considerations: Regulatory approvals, material compatibility, and quality control.