Introduction
The process of manufacturing pharmaceuticals is complex, involving a highly regulated sequential procedure of steps that guarantee the safe and effective manufacture of medicines. Beginning from the research and development phase to its final packaging and distribution, everything has been well-planned and executed with utmost care and detail. In this blog, we’ll take you through all the major stages, touching on important quality control processes.
1. Research and Development (R&D)

Pharmaceutical product development begins in the R&D laboratories. Scientists conduct extensive research for drug candidates. This stage includes:
- Identification of Target: Biological target for the drug.
- Identification of Lead Compound: Compounds associating with the target.
- Preclinical Testing: Tests conducted on laboratory and animals for safety and efficacy.
2. Clinical Trials

Once such a promising candidate is identified, it will be taken for clinical trials, which can be divided into three phases:
- Phase I: The drug is tested on a small group of healthy volunteers to determine its safety profile.
- Phase II: The drug is tested on a larger patient population to evaluate efficacy and side effects profile.
- Phase III: To further establish the effectiveness of the new drug, it undergoes massive testing with a vast population; side effects are closely monitored, and the new treatment is compared with the existing ones.
3. Manufacturing Process
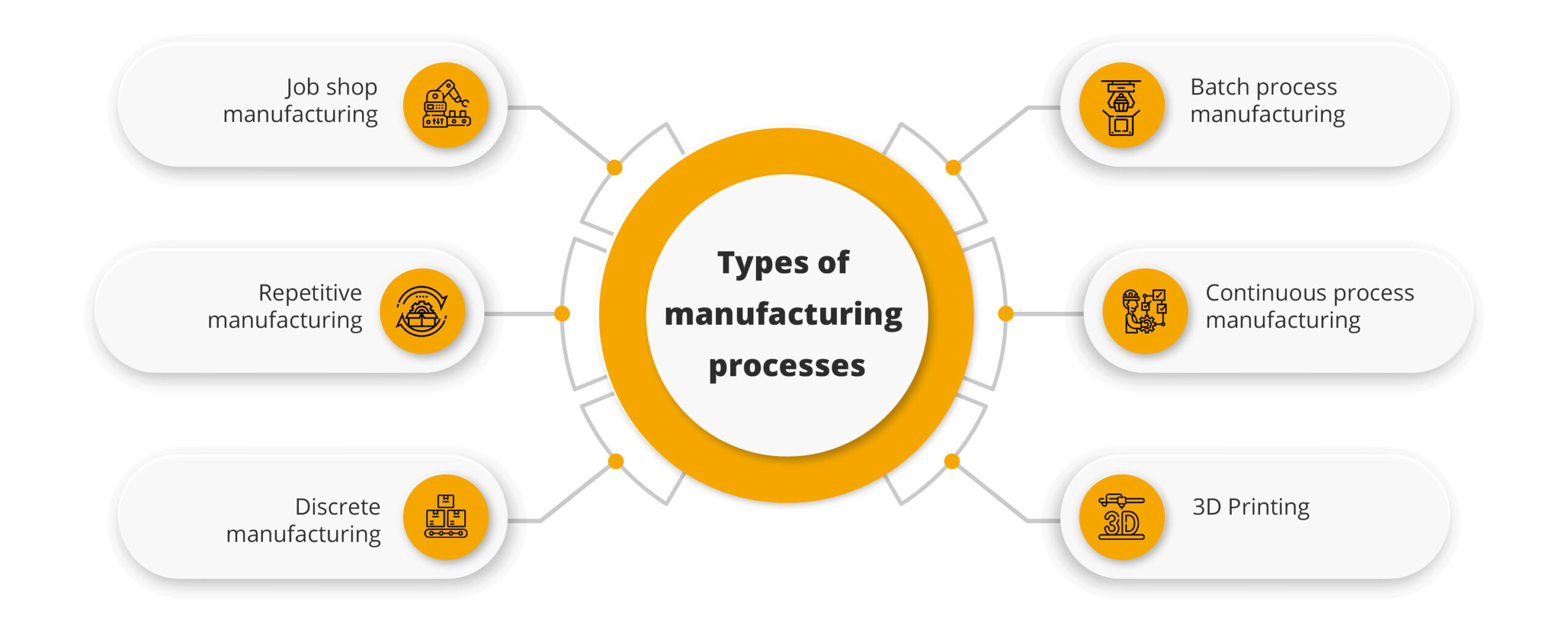
This process of manufacturing involves many steps but mainly can be divided into several key steps, including:
- Formulation: It involves the design of the drug composition with the correct mix of active ingredients and the excipients.
- Mixing and Granulation: Combining the raw materials to form a homogeneous mass.
- Drying: To evaporate the moisture and provide stability.
- Compression and Encapsulation: Compression of the mixture into tablets or encapsulation in capsules.
- Coating: Providing a coat for better stability and to manage release rate.
- Quality Control: Strict check on every batch so that they abide by the requirements, whether purity, potency, and the level of safety.
4. Packaging and Distribution
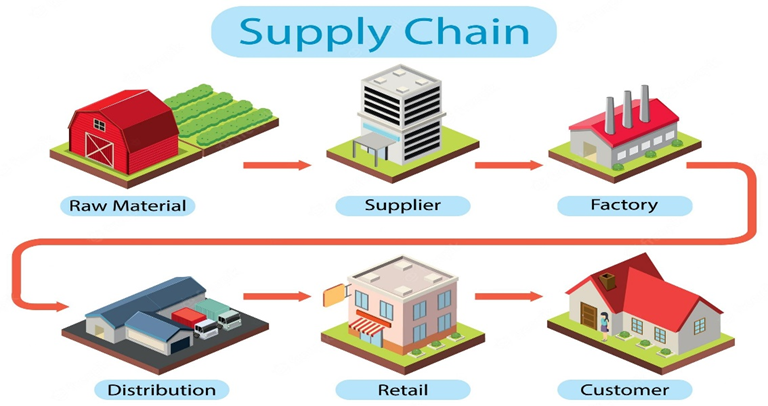
After manufacture, the drugs are packaged in appropriate containers such as blister packs and bottles. Labels containing all the necessary information are then attached, and the products are dispatched to pharmacies, hospitals, and other health-care providers.
5. Regulatory Compliance

Pharmaceutical products are rigorously regulated for safety in the medication process. Organizations such as the FDA or EMA strictly regulate pharmaceutical products from approval to further monitoring.
Conclusion
From the laboratory to the pharmacy shelf, the process for manufacturing a pharmaceutical is an extremely detailed and stringently controlled one, and each step is critical to ensure that the final product is safe, effective, and of high quality.

